Anthropology and Environmental Conservation
Environmental conservation is a critical global issue, and anthropology offers unique insights into how human societies interact with their environments. By studying cultural practices, traditional ecological knowledge, and the impacts of environmental changes on communities, anthropologists contribute to sustainable conservation efforts.

Understanding Human-Environment Interactions
Anthropologists examine the complex relationships between humans and their environments. This includes studying how different cultures perceive and interact with nature, how they manage natural resources, and how environmental changes affect their livelihoods. This holistic understanding is essential for developing conservation strategies that are culturally sensitive and effective

Traditional Ecological Knowledge
Traditional ecological knowledge (TEK) refers to the wisdom and practices developed by indigenous and local communities over generations. TEK encompasses a deep understanding of local ecosystems, sustainable resource management practices, and cultural rituals that promote environmental stewardship. Anthropologists document and promote TEK as valuable knowledge that can complement scientific approaches to conservation.

Case Study: Amazon Rainforest
One notable example of the integration of TEK in conservation efforts is the Amazon Rainforest. Indigenous communities have lived in harmony with the rainforest for centuries, developing sustainable practices that protect biodiversity. Anthropologists work with these communities to document their knowledge and advocate for their inclusion in conservation planning. This collaborative approach helps ensure that conservation strategies are both effective and respectful of indigenous rights.

Community-Based Conservation
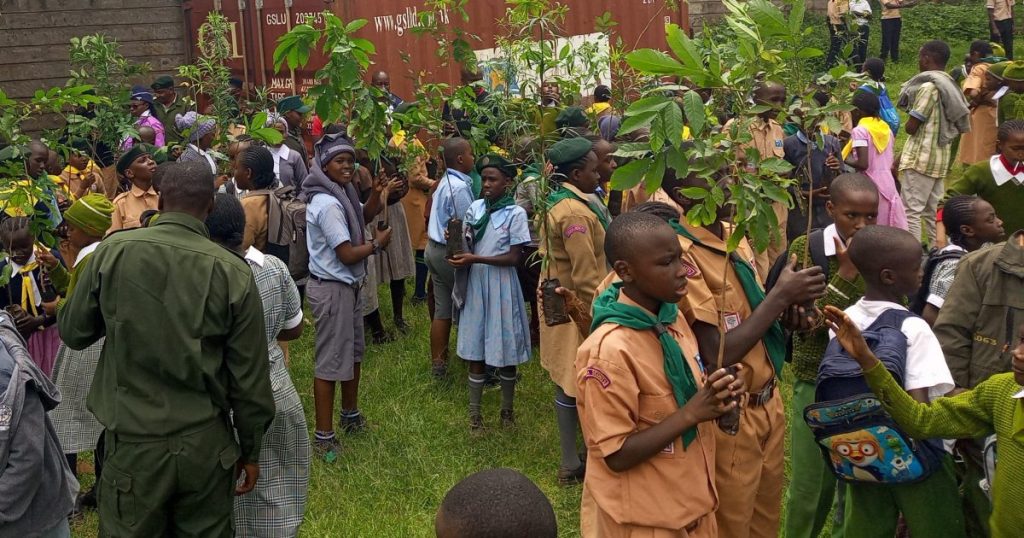
Community-based conservation (CBC) involves local communities in the planning and implementation of conservation projects. This approach recognizes that local people have a vested interest in the health of their environment and possess valuable knowledge about it. Anthropologists facilitate CBC by building trust, fostering participation, and ensuring that conservation initiatives align with community needs and values.
Challenges and Solutions
Environmental conservation faces numerous challenges, including habitat loss, climate change, and resource depletion. Anthropologists address these challenges by advocating for sustainable practices and policies that consider both environmental and social factors. For example, they may work on projects that promote agroecology, which combines traditional farming methods with scientific knowledge to enhance food security and biodiversity.
Conclusion
Anthropology provides essential insights into human-environment interactions, traditional ecological knowledge, and community-based conservation. By incorporating these perspectives, conservation efforts can become more sustainable, inclusive, and effective. Anthropologists play a crucial role in bridging cultural and scientific knowledge to protect our planet for future generations.